Civil Engineering: The Backbone of Modern Infrastructure and Innovation
Introduction

Civil engineering is the foundation of modern civilization, combining creativity and precision to design, construct, and maintain infrastructure like roads, bridges, and buildings. Civil engineers not only build physical structures but also solve environmental and social challenges.
What is Infrastructure Engineer
Infrastructure engineer is a professional discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment. This includes projects such as:
- Roads and highways
- Bridges and tunnels
- Airports and railways
- Water supply systems
- Buildings and skyscrapers
It also focuses on sustainability and safety, ensuring that projects benefit people and the planet alike.
History of Civil Engineering

Infrastructure Engineer is one of the oldest branches of engineering. From the pyramids of Egypt to the Roman aqueducts, early engineers showcased advanced construction knowledge.
With industrialization, modern civil engineering began to evolve — using scientific principles, new materials, and innovative technologies.
Branches of Civil Engineering
Infrastructure Engineer includes several sub-disciplines, each with a unique purpose and specialization:
1. Structural Engineering

Focuses on the stability and strength of buildings, bridges, and dams.
2. Transportation Engineering
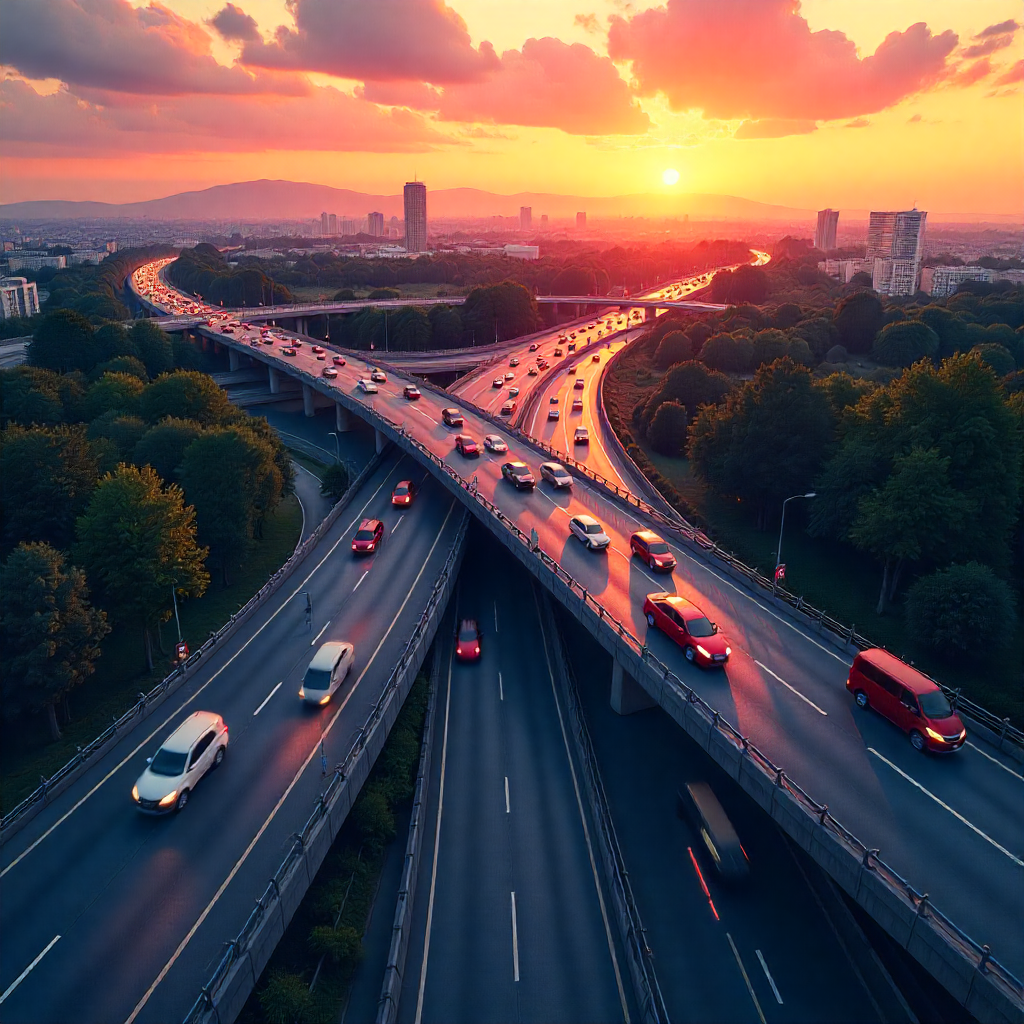

Designs efficient road networks, airports, and railway systems.
3. Geotechnical Engineering
Deals with soil behavior and foundation design.
4. Environmental Engineering

Works to improve air, water, and waste management systems.
5. Water Resources Engineering
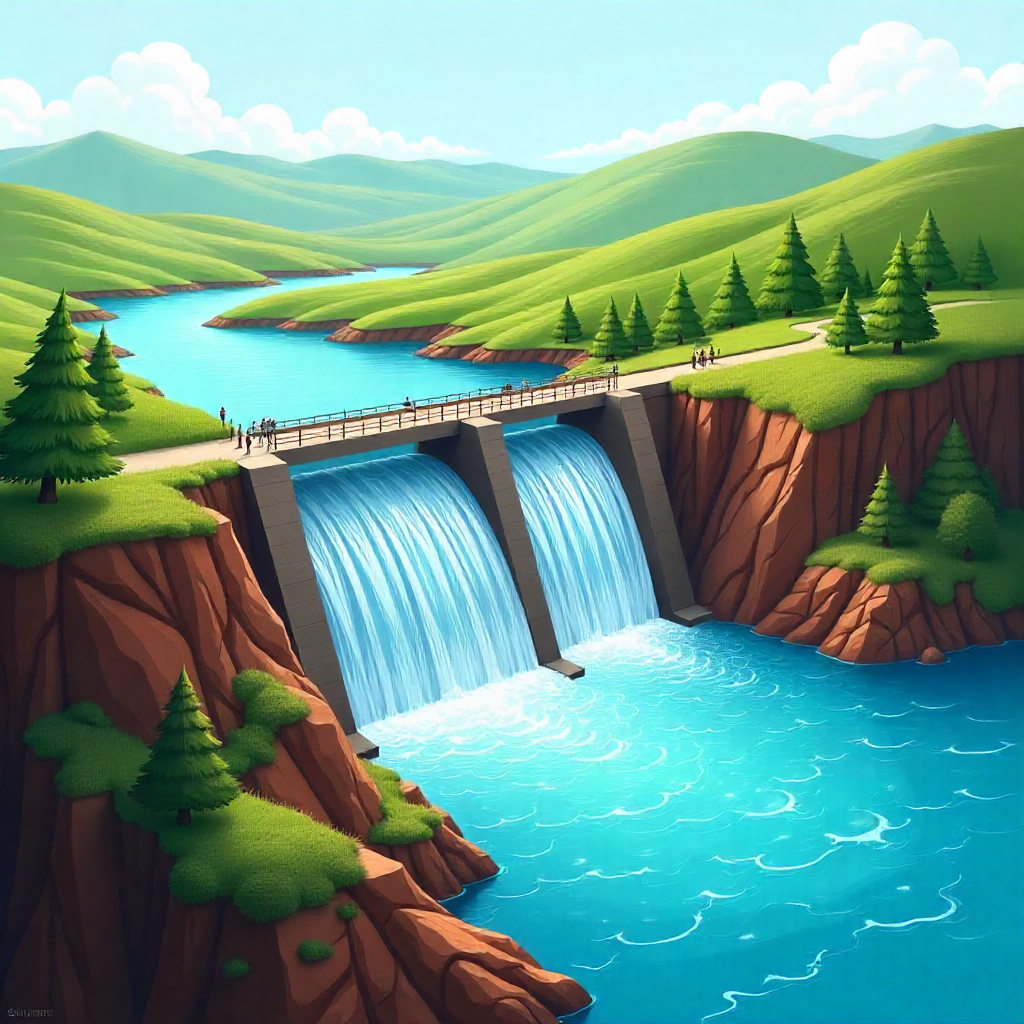

Manages hydraulic systems, including dams, canals, and flood control.
6. Construction Management

Focuses on planning, budgeting, and supervising construction projects.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A branch of engineering focused on designing, constructing, and maintaining essential infrastructure such as roads, bridges, dams, and buildings. |
| Main Branches | Structural Engineering, Geotechnical Engineering, Transportation Engineering, Environmental Engineering, Water Resources Engineering, Construction Management. |
| Key Responsibilities | Planning, designing, supervising construction, ensuring safety, sustainability, and cost efficiency. |
| Essential Skills | Mathematics, Physics, Project Management, CAD (Computer-Aided Design), Problem-Solving, Communication. |
| Tools & Software | AutoCAD, Revit, STAAD Pro, SAP2000, Civil 3D, MATLAB. |
| Work Areas | Urban development, infrastructure projects, environmental conservation, construction firms, and government agencies. |
| Educational Requirement | Bachelor’s degree in Civil Engineering (B.Sc.), with options for higher studies or professional licensure. |
| Average Salary (Global Range) | $60,000 – $100,000 per year (varies by country and experience). |
| Importance | This field shapes the built environment and ensures infrastructure supports modern life safely and efficiently. |
| Future Scope | Smart cities, green building technology, sustainable construction, and infrastructure automation. |
Importance of Construction Engineering
Construction Engineer plays a vital role in nation-building. It:
- Supports economic growth through infrastructure.
- Enhances quality of life with safe, reliable structures.
- Promotes sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Creates job opportunities and global development.
Civil engineering is not just about structures; it’s about creating safe and sustainable communities.
Career Opportunities in Civil Engineering
Infrastructure Engineer have career paths in both public and private sectors, including roles such as:
- Structural Engineer
- Site Supervisor
- Transportation Planner
- Project Manager
- Urban Planner
- Environmental Consultant
With the rise of smart cities and green technologies, the demand for Infrastructure Engineer is expected to grow significantly.
Emerging Trends in Civil Engineering

Modern civil engineering embraces technology and sustainability. Some notable trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence in design and analysis
- BIM (Building Information Modeling) for project planning
- Green Building technologies
- 3D Printing in construction
- Smart Infrastructure Systems
These innovations are shaping a safer, more efficient, and eco-friendly future.
FAQ About Civil Engineering
Q1: What is civil engineering in simple terms?
Construction Engineer is the science and art of designing and building public structures like roads, bridges, and buildings.
Q2: What are the main types of civil engineering?
The main types are structural, environmental, geotechnical, transportation, and construction management.
Q3: What skills are needed to become a civil engineer?
Analytical thinking, mathematics, project management, and creativity are essential skills.
Q4: Is Infrastructure Engineer a good career?
Yes, it’s a stable and rewarding career with global demand and opportunities for innovation.
Q5: What is the future of civil engineering?
The future lies in sustainable development, digital design tools, and smart construction technologies.
Conclusion
Civil engineering is the art of transforming ideas into reality through structures that define our cities and societies. It merges science, technology, and sustainability — making it one of the most impactful professions in the world. Whether designing bridges, managing projects, or solving environmental challenges, Building Designerremains the cornerstone of human progress.
